An ecosystem includes all of the living things (plants, animals and organisms) in a given area, interacting with each other, and also with their non-living environments (weather, earth, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere).

In an ecosystem, each organism has its’ own niche, or role to play.
Consider a small puddle at the back of your home. In it, you may find all sorts of living things, from microorganisms, to insects and plants. These may depend on non-living things like water, sunlight, turbulence in the puddle, temperature, atmospheric pressure and even nutrients in the water for life. 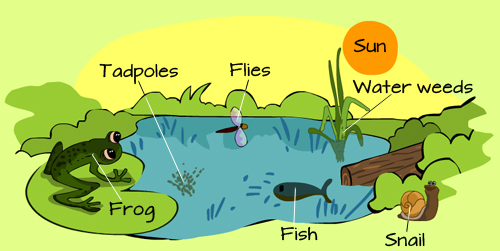
This very complex, wonderful interaction of living things and their environment, has been the foundations of energy flow and recycle of carbon and nitrogen.
Anytime a ‘stranger’ (living thing(s) or external factor such as rise in temperature) is introduced to an ecosystem, it can be disastrous to that ecosystem. This is because the new organism (or factor) can distort the natural balance of the interaction and potentially harm or destroy the ecosystem.
Usually, biotic members of an ecosystem, together with their abiotics factors depend on each other. This means the absence of one member, or one abiotic factor can affect all parties of the ecosystem.
Unfortunately ecosystems have been disrupted, and even destroyed by natural disasters such as fires, floods, storms and volcanic eruptions. Human activities have also contributed to the disturbance of many ecosystems and biomes.

|
0 comentarios